Memory
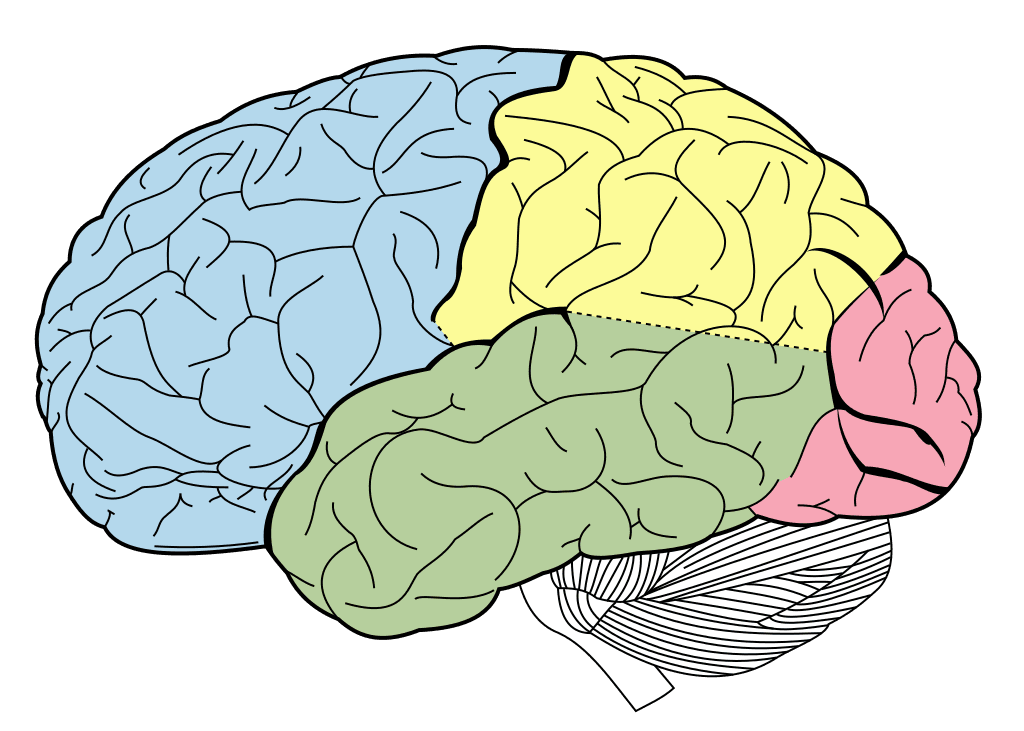
Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remembered, it would be impossible for language, relationships, or personal identity to develop. Memory loss is usually described as forgetfulness or amnesia.
- Children can 'recall early memories', Canadian study suggests
- Gene therapy 'memory boost hope'
- Why food memories are so powerful
- Brain function can start declining 'as early as age 45'
- Dreaming 'eases painful memories’
- Brain's 'atlas' of words revealed
- How can musicians keep playing despite amnesia?
- Does your brain have a mind of its own?
- 5 Mind-Melting Ways Your Memory Plays Tricks On You
- Heart pill to banish bad memories
- Beatles' tunes aid memory recall
ENGLISH COLLECTIONOCTOBER 20, 2018 AT 01:46:40 UTC